Soda cans are ubiquitous in modern society, offering quick refreshment with a pop of flavor. However, concerns regarding the health effects of soda consumption have risen in recent years. This article explores the potential harms associated with soda cans and their contents, shedding light on the health implications and offering evidence-based insights.
Understanding Soda Composition
Before diving into the health implications, it’s essential to understand what soda actually contains. Most sodas share common ingredients, including:
- Carbonated water: This is the primary component of all sodas.
- High fructose corn syrup (HFCS) or sugar: These sweeteners contribute to the beverage’s taste but also its calorie count.
- Acids: Phosphoric acid and citric acid are common, contributing to the tangy flavor and acidity.
- Caffeine: Many sodas contain caffeine, a stimulant that can affect energy levels and alertness.
- Preservatives and colorings: Ingredients like sodium benzoate and artificial colors enhance flavor and appearance.
While these components create an enjoyable beverage, they also raise health concerns.

The Sugar Content Dilemma
One of the most alarming aspects of soda cans is their high sugar content. A standard 12-ounce soda can contain about 39 grams of sugar, equating to roughly 10 teaspoons.
Health Risks Associated with High Sugar Intake
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to various health issues:
- Obesity: High-calorie drinks contribute to weight gain. Studies show that sugary beverages significantly increase the risk of obesity among children and adults.
- Diabetes: Regular consumption of sugary drinks can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Research indicates that individuals who consume one or more sugary drinks daily have a 26% higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Disease: High sugar intake can elevate blood pressure and lead to chronic inflammation, increasing the risk of heart disease.
The table below summarizes the sugar content in various popular sodas:
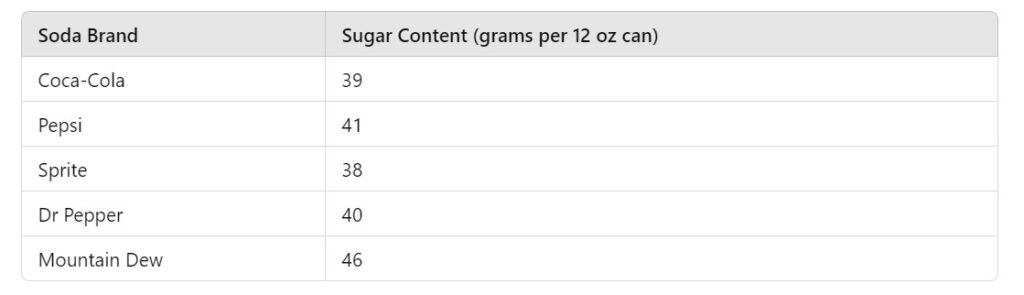
This data illustrates just how much sugar can be found in a single can of soda, reinforcing the need for moderation.
The Impact of Caffeine
Caffeine is another common ingredient in many soda cans. While moderate caffeine consumption can be safe for most people, excessive intake can lead to adverse effects.
Potential Risks of High Caffeine Intake
- Increased Heart Rate: High caffeine consumption can lead to palpitations and increased heart rate.
- Anxiety and Insomnia: Excessive caffeine can contribute to anxiety and disrupt sleep patterns.
- Dependence: Regular intake can lead to caffeine dependence, causing withdrawal symptoms such as headaches and irritability.
According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, moderate caffeine consumption (about 400 mg daily) is generally safe for most adults. However, many sodas contain around 30-55 mg of caffeine per can, which can add up quickly if consumed in large quantities.
Acidity and Dental Health
The acidity of soda is another concern. The presence of phosphoric and citric acids can erode tooth enamel, leading to dental issues over time.
The Effect on Teeth
A study published in the Journal of the American Dental Association found that soda consumption is linked to dental erosion. Regular exposure to acidic drinks can weaken enamel, making teeth more susceptible to cavities and decay.
Moreover, sodas can contribute to dry mouth, further compounding dental health issues. This condition decreases saliva production, which is crucial for neutralizing acids in the mouth.
Environmental Concerns
While this article primarily focuses on health implications, the environmental impact of soda cans cannot be ignored. The production and disposal of aluminum cans raise sustainability issues.
Recycling and Waste
Aluminum cans are recyclable, but many end up in landfills. According to the Aluminum Association, about 75% of all aluminum ever produced is still in use today, highlighting the importance of recycling. However, consumer habits often lead to wasted resources, emphasizing the need for greater awareness and responsible disposal.
Moderation: The Key to Enjoyment
Despite the potential harms associated with soda cans, moderation is critical. Enjoying a soda occasionally may not lead to significant health issues. The real risk arises from regular, excessive consumption.
Tips for Moderation
- Opt for Smaller Sizes: Choose smaller cans or bottles to limit intake.
- Dilute with Water: Mix soda with water or ice to reduce sugar concentration.
- Explore Alternatives: Consider healthier options like sparkling water or natural fruit juices.
Conclusion
Soda cans, while convenient and enjoyable, can pose several health risks if consumed excessively. High sugar and caffeine content, combined with acidity, can lead to obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and dental problems. Therefore, it’s essential to consume sodas in moderation and consider healthier alternatives. By making informed choices, you can enjoy the occasional soda without compromising your health.

FAQs
1. Are all sodas equally harmful?
Not all sodas are created equal. Diet sodas have fewer calories but may contain artificial sweeteners that some people prefer to avoid.
2. How does soda contribute to weight gain?
Sodas are high in sugar and calories, providing empty calories that do not satisfy hunger, often leading to overeating.
3. Can occasional soda consumption be healthy?
Occasional consumption is generally not harmful for most people, especially when balanced with a healthy diet.
4. What are the alternatives to soda?
Consider options like sparkling water, herbal teas, or infused water for a refreshing, healthier choice.
5. How can I protect my teeth if I drink soda?
Rinse your mouth with water after consuming soda, and maintain a regular dental hygiene routine to protect your teeth.
6. Is caffeine in soda dangerous?
Moderate caffeine intake is safe for most people. However, excessive consumption can lead to adverse effects like anxiety and sleep disturbances.





